Detecting hydrocarbon pollutants in groundwater
A major environmental and health challenge taken up by FEMTO-ST researchers working with TotalEnergies
BTEX (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylenes) are hydrocarbon-based pollutants found in groundwater near industrial sites and service stations. Classified as toxic substances, some are even recognized as carcinogens. Their rapid and accurate detection is therefore essential to preserve water resources and protect human health. To meet this challenge, FEMTO-ST researchers, in collaboration with TotalEnergies, have developed a new generation of sensors capable of identifying these pollutants at very low concentrations. This major technological advance paves the way for more effective monitoring and better-targeted pollution control strategies.
A double innovation for ultra-efficient detection
BTEX molecules are not very reactive, which makes them difficult to detect and even more complex to eliminate. To circumvent this obstacle, the researchers exploited supramolecular interactions specific to the aromatic rings of these compounds. By designing and synthesizing a polymer optimized for these interactions, they were able to deposit an ultra-sensitive nanometric layer on the active surface of a sensor.
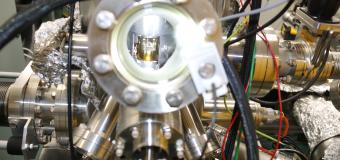
But that's not all: detecting pollutants in groundwater also poses a technical challenge, as sensors must be autonomous, robust and remotely interrogatable. To meet these requirements, the research team opted for surface-elastic acoustic sensors. Using a substrate made of lithium tantalate, a piezoelectric material, they succeeded in designing a device capable of operating directly in an aquatic environment, without loss of the acoustic signal.
Unprecedented performance and concrete applications
Thanks to this approach combining supramolecular chemistry and acoustic sensor engineering, the researchers have achieved exceptional sensitivity, enabling BTEX to be detected at concentrations below 0.5 ppm - the limit imposed by environmental agencies. This scientific breakthrough has already led to the filing of two patents and one scientific publication.
Towards real-time groundwater monitoring
L’objectif désormais est de tester ces capteurs en conditions réelles, directement dans le sous-sol et sur de longues périodes. À terme, le déploiement d’un réseau de capteurs sur des sites industriels pourrait révolutionner la surveillance des eaux souterraines, en offrant une solution fiable et continue pour détecter et prévenir la contamination par les hydrocarbures.
Contacts :
Jean-Michel Friedt (FEMTO-ST)
Frédéric Chérioux (FEMTO-ST)
Nathalie Nief (TotalEnergies)
More informations : ACS Publications 10.1021/acsomega.4c08826
[[{"fid":"40504","view_mode":"default","fields":{"format":"default","alignment":"","field_file_image_alt_text[und][0][value]":false,"field_file_image_title_text[und][0][value]":false,"external_url":""},"type":"media","field_deltas":{"1":{"format":"default","alignment":"","field_file_image_alt_text[und][0][value]":false,"field_file_image_title_text[und][0][value]":false,"external_url":""}},"attributes":{"class":"media-element file-default","data-delta":"1"}}]]
Detection of BTEX in water by supramolecular recognition