Imaging quantum interference of entangled photon pairs of extremely high dimensionality
Researchers from the Optics Department have developed an imaging device allowing the spatial and temporal resolution of the phenomenon of quantum interference between pairs of entangled photons of extremely high dimensionality. This work paves the way for the development of very high dimensional information protocols.
In a crystal, photons of a laser beam can split in pairs of lower frequency, the spontaneous down conversion (SPDC) phenomenon. The so-called twin, or entangled, photons of a pair form a single quantum object. Therefore, if they are sent on a beam-splitter they exit randomly, but both on the same output port. This is the famous Hong-Ou-Mandel (HOM) two-photon interference.
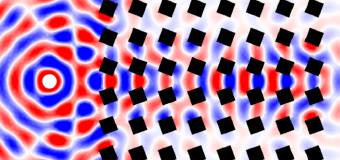
HOM interference is used in novel communication protocols, like quantum teleportation and quantum information processing, but until now without spatial resolution, by using bucket detectors. However, entanglement concerns all properties of twin photons, including their position in space and time, and here HOM interference is obtained for thousands of spatial as well temporal resolution cells, resulting in a total spatio-temporal dimensionality of 3 million.
In our HOM interferometer, spatial coincidences at the output ports are imaged on two cameras operating in photon counting mode. Since we control temporally, spatially, in polarization and in wavelength the indistinguishability between the photons of a pair, we have observed and quantified spatially and temporally the HOM interference at the quantum level, with a visibility of 60%, of more than 4000 photon pairs of extremely large spatio-temporal dimensionality.
Given the essential role played by two-photon HOM interference in most of the systems developed for quantum information processing, demonstrating that HOM interference can be obtained by manipulating quantum states of giant dimensionality opens the way for the development of very high-dimensional quantum information protocols using space and time variables.
This work has just been published in the journal Physical Review X and is highlighted in the CNRS news
Contact : Fabrice Devaux
Référence :
Imaging spatio-temporal Hong-Ou-Mandel interference of biphoton state of extremely high Schmidt number, F. Devaux, A. Mosset P.A. Moreau, et E.Lantz .
Physical Review X, 2020.
DOI : 10.1103/PhysRevX.10.031031