The fastest pick-and-place robot in the world
A research team has developed a miniature robot capable of manipulating micrometric objects at unprecedented speeds. This work has been published in the prestigious American journal "Science Robotics"
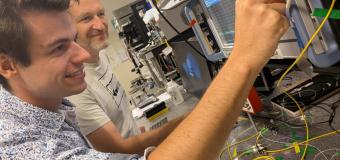
Speed and precision are two major issues in robotics and in Industry of the Future (also known as Industry 4.0). Within this framework, RoMoCo research team of AS2M department at FEMTO-ST Institute has developed a unique robot.
MiGriBot is a miniature robot able to perform pick-and-place operations of sub-millimeter objects at unpresented speeds. These performances are made possible thanks to its original and unique architecture that allows it to grip and manipulate micro-objects barely visible to the naked eye (from 40 micrometers to several hundred micrometers). In fact, where other microrobots have a rigid end-effector, MiGriBot is based on a new principle with an articulated end. This articulated end allows to drive a microgripper without any wire or embedded actuator! The second advantage of this robot is that all its degrees of mobility, including the ones from the microgripper on the articulated end, are operated from the base of the robot, making its mobile parts very lightweight. Finally, its robotic structure occupies a surface of only 20 x 20 mm2. This level of compactness is achieved by using Silicon for the rigid elements, a polymer (Polydimethylsiloxane - PDMS) as flexible joints and piezoelectric actuators equipped with position sensors. MiGriBot is therefore lighter, more compact and faster than existing robotic micro-manipulators.
[[{"fid":"11000","view_mode":"default","fields":{"format":"default","alignment":"","field_file_image_alt_text[und][0][value]":false,"field_file_image_title_text[und][0][value]":false,"external_url":""},"type":"media","field_deltas":{"2":{"format":"default","alignment":"","field_file_image_alt_text[und][0][value]":false,"field_file_image_title_text[und][0][value]":false,"external_url":""}},"attributes":{"class":"media-element file-default","data-delta":"2"}}]]
Contact : Redwan DAHMOUCHE
[[{"fid":"10997","view_mode":"default","fields":{"format":"default","alignment":""},"link_text":"Read the press release (in french)","type":"media","field_deltas":{"1":{"format":"default","alignment":""}},"attributes":{"class":"media-element file-default","data-delta":"1"}}]]
See the vidéo presentation of MiGriBot