Nanorobotics of the future: FEMTO-ST enters the 4th dimension
For the first time, nanorobotic structures have been realized by folding in 3 dimensions a multilayer membrane and proposing their actuation by an electro-thermo mechanical principle.
Published in "Advanced Materials", this work is in line with the latest innovations of FEMTO-ST, and more particularly of the members of the CMNR - Centre de Micro et Nano Robotique - which has just been created and in which we find the µRobotex platform, initially labelled in the framework of the PIA I and which became TIRREX, in January 2021, in the framework of the PIA III.
This article is based on the innovations tha led to the fabrication of a micro-house by origami in 3 dimensions from a silica membrane as welle as the world record of the smallest volume character ever animated in stop motion.
In this new experiment, the challenge goes far beyond the origami folding of the micro-house, since the work allows to realize for the first time nanorobotic structures (in the article, a clamp is used as a demonstrator) of dimensions smaller than 100 µm by folding in 3 dimensions a multilayer membrane. The actuation of these 3D structures is performed by an electro-thermo-mechanical principle which leads to what is called, in this microtechnical context, "the 4th dimension", i.e. the actuation in addition to the fabrication of a 3D structure. The challenge successfully achieved is significant: not only is it difficult to bend the multilayer structure by focused ion bombardment, mostly composed of silica, at 90° but also to integrate the actuation of the fingers of a new microgripper by innovative bending at this scale.
One of the scientific contributions of the work published in this article lies in the detailed understanding of the physical phenomena occurring during bidirectional folding assisted by focused ion bombardment (FIB). This is the result of intense collaborations useful for the multiphysical modeling of phenomena specific to multidisciplinary work such as nanorobotics and has led to the proposed technology being reproducible, mastered and applicable to many other problems than robotics.
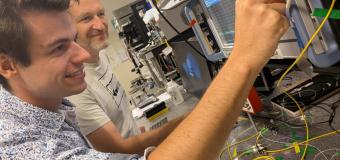
All the work has been done at FEMTO-ST, by researchers of the AS2M department, from design to functional tests, including modeling and of course manufacturing. The fabrication steps of the silica membranes and the aluminium electrode deposits according to predefined patterns have been realized in the FEMTO-ST MIMENTO plant from masks designed in-house. The ion beam machining leading to the 3D and 4D structures was performed on the µRobotex platform. All the steps of functional tests, visualization of finger deformations and measurements of amplitudes and aperture accuracies were also performed on the µRobotex platform.
This work responds to a growing need for systems that allow gripping on small scales, because in the race to miniaturize systems and components, it is essential to have high-performance, perfectly controllable, precise, reproducible and robust gripping means over time. This type of gripper has been created to allow the manipulation of isolated molecules (10 to 50 nm), viruses (20 to 200 nm), nanotubes (25 to 150 nm), bacteria (1 to 10 µm), globules (1 to 3 µm), micro and nano components of electrical and optical circuits The application example described in the paper is a gripper used to move a stretched optical fiber with a diameter of 6 to 8 µm.
To push the limits of this research result, it would now be interesting to integrate a means of measuring the forces applied to the manipulated objects. This information would allow to increase the dexterity of manipulation and to extend the range of grasped objects by having the possibility to grasp soft materials without damaging them. For specific applications, it would also be possible to functionalize the fingertips of the microgrips in order to selectively pick up certain objects in certain solutions.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202103371
Acknowledgements :
This work was made possible thanks to the involvement of many staff members of the FEMTO-ST institute, its supervisory bodies (CNRS, UBFC, UFC, ENSMM), its technology centers (MIMENTO, Rénatech network and Robotex/Tirrex) and the financial support of the Burgundy Franche-Comté region as well as the French National Research Agency, in particular via the EUR Eiphi project "Nanofolding".