A novel approach to filling miniature atomic clock cells
This new method, which gains flexibility, paves the way for large-scale production of atomic sensors.
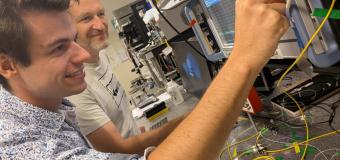
In recent years, the development of miniature atomic instruments with high sensitivity and accuracy such as clocks or magnetometers is experiencing a real boom. Miniature atomic clocks are intended for example for telecommunications or navigation equipment. These instruments are generally based on the interrogation of a set of alkaline atoms in vapour phase within a cell of millimetre dimensions, generated by micro-fabrication techniques and composed of glass and silicon. One of the difficulties lies in filling these cells with various species (alkaline metals and buffer gases) while preserving the purity and stability of their internal atmosphere over time.
In this context, the work published by FEMTO-ST in Nature Microsystems & Nanoengineering and entitled "Wafer-level vapor cells filled with laser-actuated hermetic seals for integrated atomic devices" proposes a new cell filling technique, inspired by those used for the realization of traditional centimetric glass cells produced by glass blowing, but adapted to microfabrication techniques. This technique is based on micro devices structured in glass and silicon similar to valves that can be operated by laser.
Contact : Nicolas Passilly